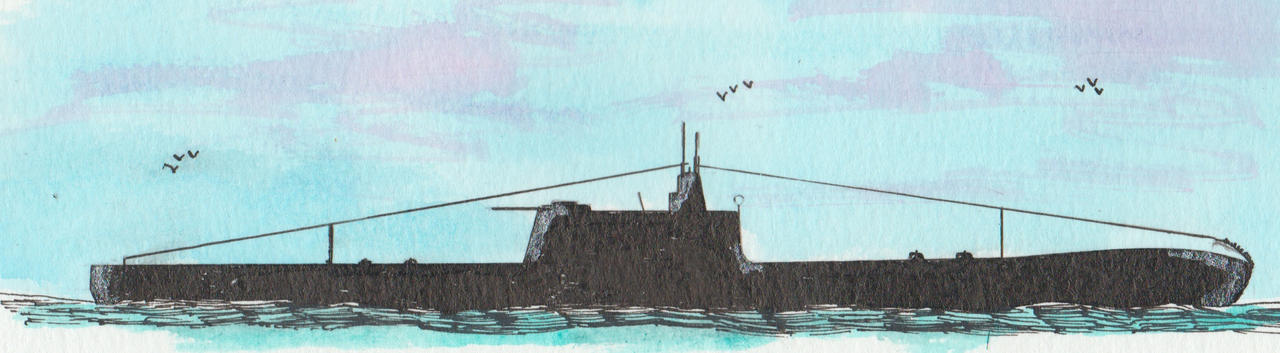
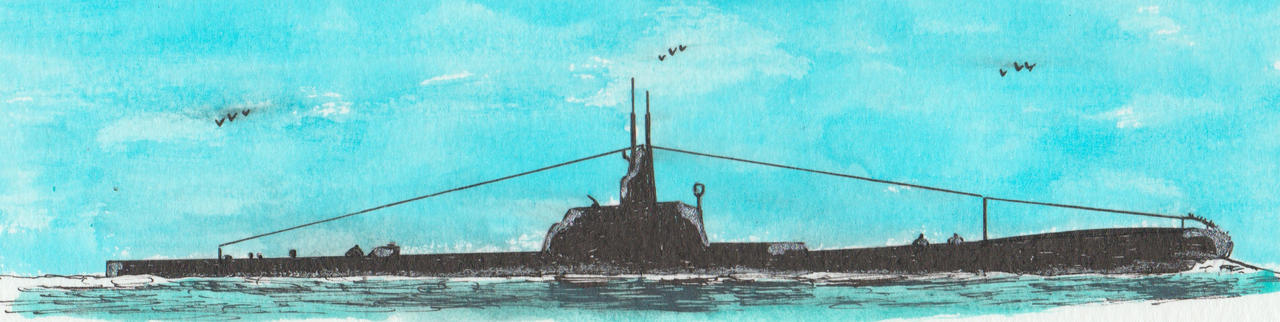
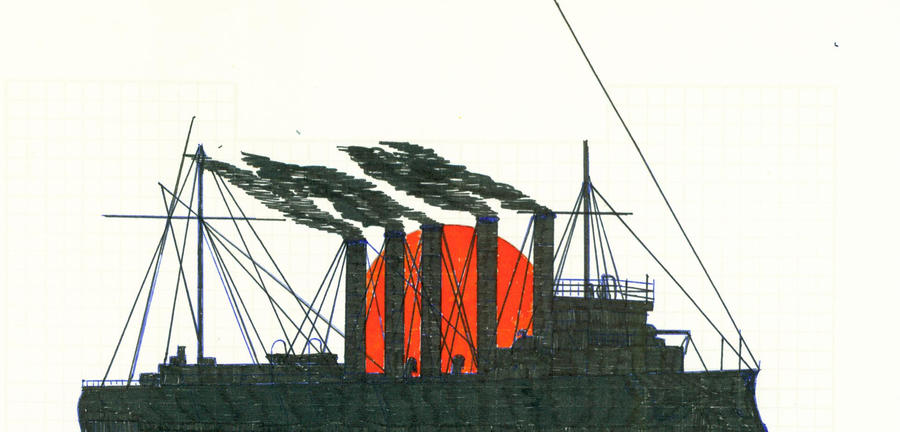
HMS Hood. ©Warshipsresearch.blogspot.com
Pre-design. ©Warshipsresearch.blogspot.com
Preceded by Admiral-class. Legend displacement 46,500 tons and as dimensions 850 x 106 x 33 feet. Equipment 1,000 tons, fuel 1,200 tons, margin 230 tons, armament 7,400 tons, machinery ect. 6,430 tons, armor &protection 13,350 tons and hull 16,890 tons. Armament consisted of 3x3-16.5” cal 45 guns, 16-6” guns, 5x4.7” anti aircraft guns, 4 multiple pom-poms and 2 torpedo tubes. Horsepower 180,000 shp and speed of 33 knots. Armor 14” thock belt reduced to 12” by boiler and engine rooms, inclined at 25 degrees. Bulkheads 12” forward, 10” aft inclined at 25 degrees. Barbettes 14”, conning tower 12” 9 “roof. Torpedo bulkhead 1.75”. And an armour deck
Sources
Brown, D.K. Nelson to Vanguard.
Brown, D.K. A Century of naval construction. The history of the Royal Corps of naval constructors.
Breyer, Siegfried. Battleships and battle cruisers, 1905-1970.
Burt, R.A. British Battleships 1919-1945.
Campbell, N.J.M. “Washington’s Cherrytrees. The evolution of the British 1921-1922 Capital Ships”, in: Warship, Vol. 1-4.
Friedman, Norman. British Battleships 1906-1946.
Johnston, Ian and Ian Buxton. The Battleship Builders.
Parkes, Oscar. 1860-1950. A History of Design, Construction and Armament British Battleships.
Raven, Alan and John Roberts. British battleships of World War Two.
Stern, Robert C. The Battleship Holiday. The Naval Treatries and Capital Ship Design.
Papers Sir Eustace Tennyson D'Eyncourt, Royal Museums Greenwich.
Warshipsresearchblogspot.com
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/G3_battlecruiser checked 27-2-2026