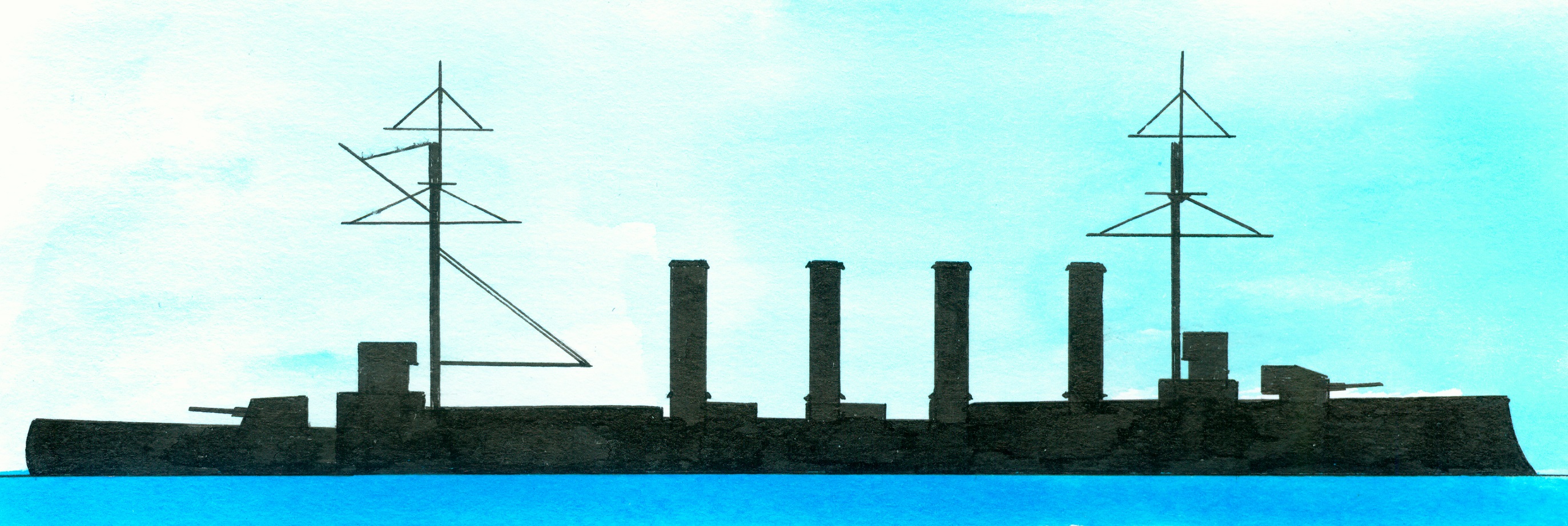
Laid down at the shipyard of Fairfield Shipbuilding&Engineering, Govan, Scotland on 11 September 1899, renamed Good Hope on 2 October 1900, launched on 21 February 1901, completed on 8 November 1902, added to the reserve in 1913, decommissioned in mid 1914 and sunk in the Battle of Coronel of the Chilean coast in a battle with the German East Asia squadron which included the large armoured cruisers Scharnhorst (1) and Gneisenau (2) on 1 November 1914. Building costs 990.759-1.023.629 pound sterling.
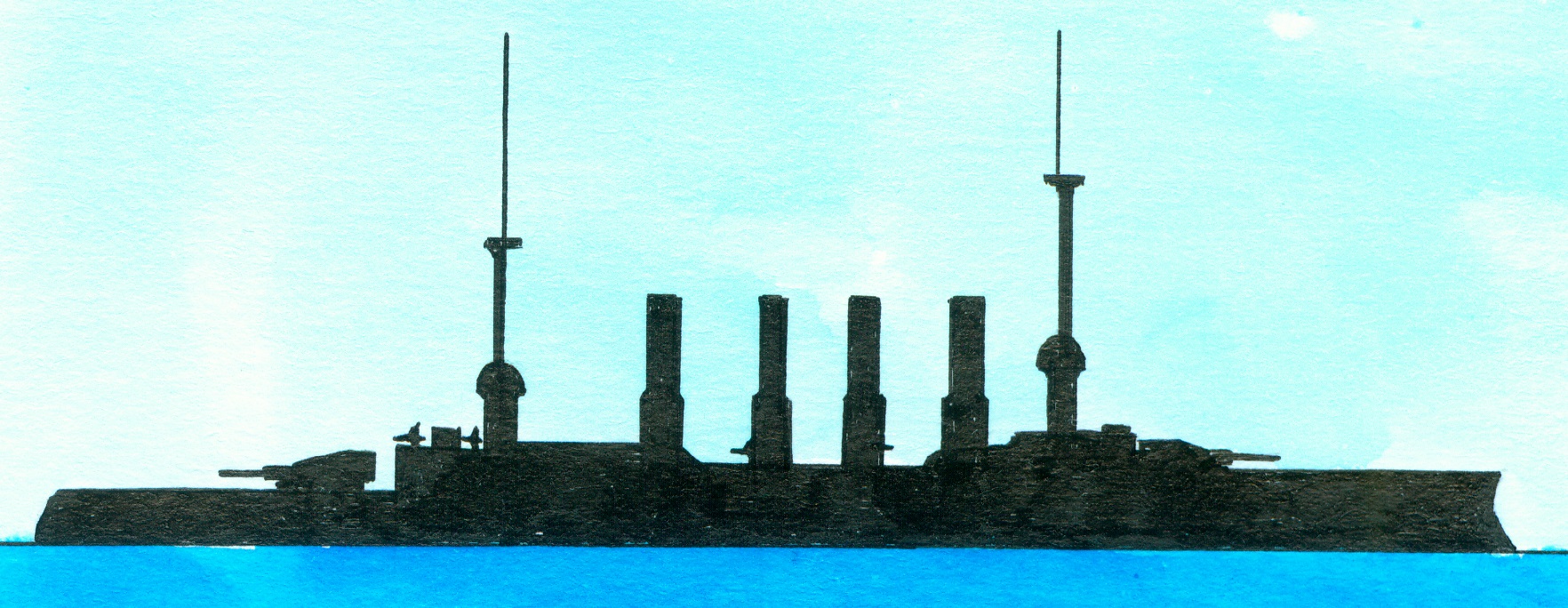
German SMS Scharnhorst and Gneisenau
Of the Drake-class consisting of the Drake, Good Hope, King Alfred and Leviathan preceded by the Cressy-class and succeeded by the Monmouth-class. In fact was this class an enlarged and improved Cressy-class design made by chief constructor Sir William White with as potential opponent the French armoured cruiser Jeanne d’Arc.(3)
French Jeanne d'Arc
General technical specifications. Displacement 14.380/14.150 long tons (normal) and as dimensions 162,6 (over all) x 21,7 x 7,9 metres or 533.6 x 71.4 x 26 feet. The 2-4 cylinder triple expansion engines and 43 Belleville boilers supplied via 2 shafts 30.000 ihp allowing a speed of 23 knots (design). Maximum coal bunker capacity 2.500 ton. Their crew numbered 900 men. The armour consisted of a 5,1-16,2cm/2-6” thick belt ending in 12,7cm/5” thick bulkheads, 2,5-6,4cm/1-2,5” thick decks, with the gun turrets, barbettes and conning tower all protected by 15,2cm/6” thick armour. The armament consisted of 2x1-23,4cm/9.2” breech loading Mk X guns, 16x1-15,2cm/6” breech loading Mk VII guns in barbettes, 12x1-7,6cm/3” quick firing 12 cwt guns. 3-4,7cm quick firing Hotchkiss guns and 2x1-45cm/18” submerged torpedo tubes.
Notes
1. Laid down at the shipyard of Blohm&Voss, Hamburg, Germany with yard number 175 on 3 January 1905, launched on 22 June 1906, commissioned on 24 October 1907 and sunk in a battle with the British fleet during the so-called Battle of the Falkland Islands on 8 December 1914. Of the Schanhorst-class consisting of the Scharnhorst and the Gneisenau. Preceded by the Roon-class and succeeded by the SMS Blücher. General technical specifications of this class. Displacement 11.616 tons/11.433 long tons12.804 short tons (standard)-12.985 tons/12.780 long tons/14.314 short tons (full load) with as dimensions 143.8 (waterline) 144,6 (overall) x 21,6 x 8,37 metres or 472-474.5 x 70.10 x 26.6 feet. The 3 shaft triple expansion engines and 18 water-tube boilers supplied 26.000 ihp (design) allowing a speed of 22,7 knots; during the trials 28.782 ihp and a speed of 23m5 knots. Coal bunker capacity 800 tons/880 short tons (standard)-2.000 tons/2.200 short tons (maximum). Range with a cruising speed of 12 knots was 4.800 nautical miles. Their crew numbered 840 men (included 52 officers). The armour consisted of a 15cm/5.9” thick belt, a 3,5-6cm/1.4-2.4” thick deck and with the gun turrets protected by 18c,/7.1” thick armour. The armament consisted of 2x4&4x1-21cm/8.3” L/40 quick firing guns, 6x1-15cm/5.9” L/40 quick firing guns, 18x1-8,8cm/3.5” guns and 4-45cm/18” submerged torpedo tubes (1x bow, 2 sides, 1 stern).
2.. Laid down at the shipyard of AG Weser, Bremen, Germany with yard number 144 on 28 December 1904, launched on 14 June 1906, building costs more as 19 million goldmarks, commissioned on 6 March 1908 and sunk in a battle with the British fleet during the so-called Battle of the Falkland Islands on 8 December 1914
3. With a displacement of 11.300 tons/11.122 long tons and as dimensions 145 x 19,4 x 8,1 metres or 475.9 x 63.8 x 26.7 feet. Speed 21,8 knots. Armament consisted of 2-19,4cm/7.6” guns and 14-13,8cm5.4” guns.